The Spindle Apparatus: The Organelle That Moves Chromosomes During Cell Division
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division that are essential for growth, development, and reproduction. Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four haploid daughter cells. Both mitosis and meiosis involve the movement of chromosomes, which are structures that contain the cell's genetic material. During mitosis, the chromosomes are moved by a structure called the spindle apparatus which is composed of microtubules. During meiosis, the chromosomes are moved by a structure called the synaptonemal complex.
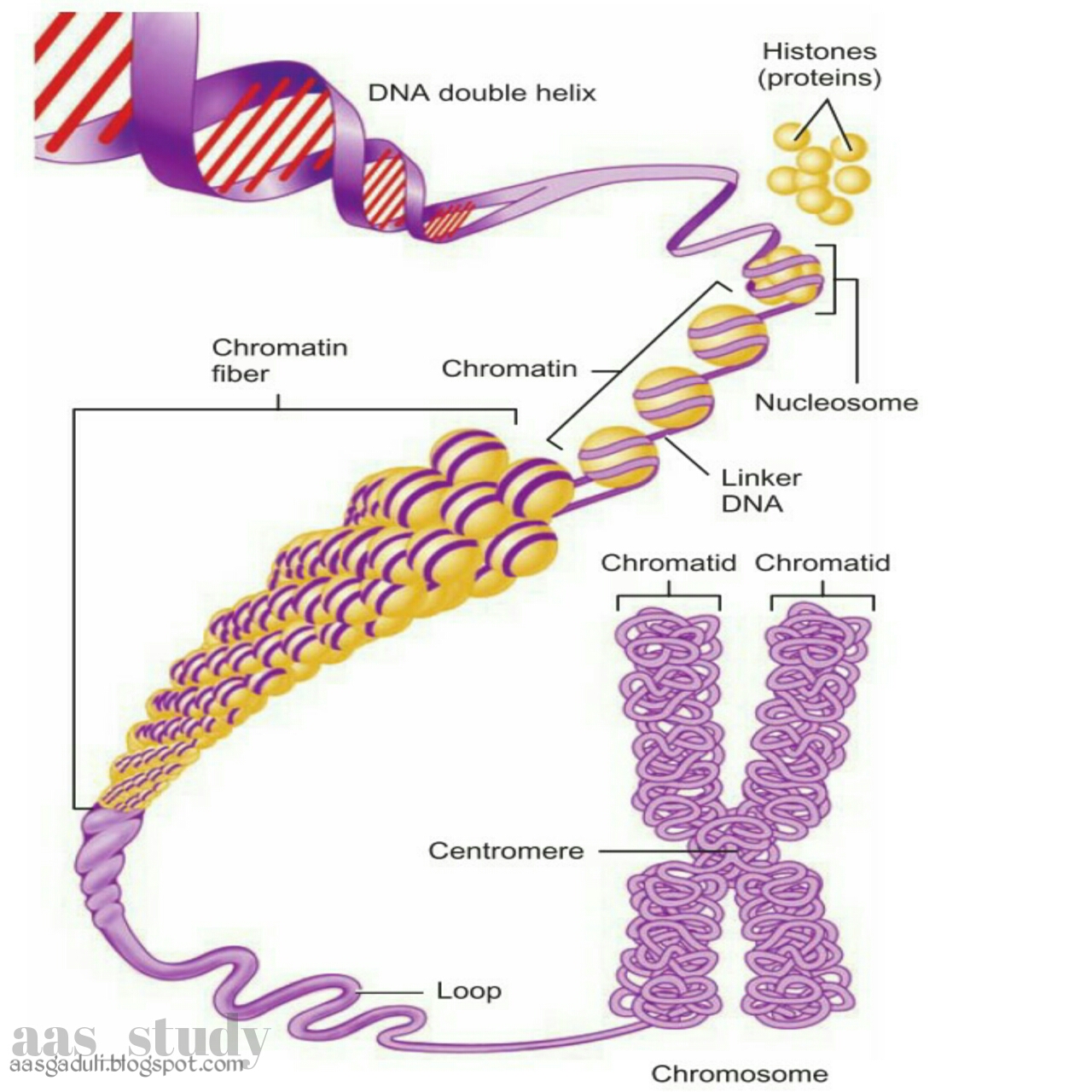
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
The synaptonemal complex is a structure that is composed of proteins and RNA. It forms between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. The synaptonemal complex helps to align the chromosomes and to ensure that they are properly separated during meiosis.
The movement of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis is essential for the proper division of the cell. If the chromosomes are not moved correctly, the daughter cells will not receive the correct amount of genetic material. This can lead to a variety of problems, including birth defects, developmental disorders, and cancer.
""what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle"
The movement of chromatids during cell division is a critical process for ensuring the proper distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. This process is facilitated by a structure called the spindle apparatus. The spindle apparatus is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
- Structure: The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins.
- Function: The spindle apparatus is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division.
- Regulation: The spindle apparatus is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle and the presence of DNA damage.
- Evolution: The spindle apparatus is a highly conserved structure that is found in all eukaryotes.
- Medical relevance: Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer.
- Research: The spindle apparatus is a major area of research in cell biology.
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It ensures that the chromosomes are properly distributed to daughter cells, which is essential for the proper development and function of the organism.
Structure
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. It is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
The spindle apparatus is essential for the proper distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells. If the spindle apparatus is not functioning properly, the chromosomes may not be moved correctly, which can lead to genetic disorders such as aneuploidy and cancer.
The structure of the spindle apparatus is highly conserved across all eukaryotes. This suggests that the spindle apparatus is essential for cell division and that it has been conserved throughout evolution.
The study of the spindle apparatus is a major area of research in cell biology. Scientists are working to understand the structure and function of the spindle apparatus and how it is regulated. This research is important for understanding the fundamental processes of cell division and for developing new treatments for genetic disorders.
Function
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. It is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
- Role in cell division: The spindle apparatus is essential for the proper distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells. If the spindle apparatus is not functioning properly, the chromosomes may not be moved correctly, which can lead to genetic disorders such as aneuploidy and cancer.
- Examples: The spindle apparatus is found in all eukaryotes, which are organisms that have cells with a nucleus. Some examples of eukaryotes include plants, animals, and fungi.
- Implications for "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle": The spindle apparatus is the organelle that moves the chromatids around during cell division. Chromatids are the individual strands of DNA that make up a chromosome. During cell division, the chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell. The spindle apparatus is responsible for this movement.
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It ensures that the chromosomes are properly distributed to daughter cells, which is essential for the proper development and function of the organism.
Regulation
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. It is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The spindle apparatus is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle and the presence of DNA damage.
- Cell cycle: The spindle apparatus is regulated by the cell cycle. The cell cycle is a series of events that occur in a cell leading to its division and duplication. The spindle apparatus is assembled during prophase and metaphase of the cell cycle. It is then disassembled during anaphase and telophase.
- DNA damage: The spindle apparatus is also regulated by the presence of DNA damage. DNA damage can occur due to a variety of factors, such as exposure to radiation or chemicals. If the DNA is damaged, the spindle apparatus will not be able to function properly, which can lead to cell death.
The regulation of the spindle apparatus is essential for the proper division of cells. If the spindle apparatus is not regulated properly, the chromosomes may not be moved correctly, which can lead to genetic disorders such as aneuploidy and cancer.
Evolution
The spindle apparatus is a highly conserved structure that is found in all eukaryotes. This means that it has been passed down from a common ancestor and has not changed much over time. This suggests that the spindle apparatus is essential for cell division and that it has been conserved throughout evolution.
The spindle apparatus is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. It is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
The spindle apparatus is essential for the proper distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells. If the spindle apparatus is not functioning properly, the chromosomes may not be moved correctly, which can lead to genetic disorders such as aneuploidy and cancer.
The conservation of the spindle apparatus across all eukaryotes suggests that it is an essential structure for cell division. This understanding is important for understanding the fundamental processes of cell division and for developing new treatments for genetic disorders.
Medical relevance
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer.
Aneuploidy is a condition in which a cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. This can occur due to defects in the spindle apparatus, which can lead to chromosomes being lost or duplicated during cell division. Aneuploidy can have a variety of effects on the organism, including birth defects, developmental disorders, and cancer.
Cancer is a disease in which cells grow and divide uncontrollably. Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to cancer by allowing cells to divide without properly distributing their chromosomes. This can lead to the development of tumors and the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
The study of the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
Research
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer.
Research on the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
One of the main goals of research on the spindle apparatus is to understand how it is regulated. The spindle apparatus is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle and the presence of DNA damage. By understanding how the spindle apparatus is regulated, scientists can develop new ways to control cell division.
Another goal of research on the spindle apparatus is to develop new drugs that can target the spindle apparatus. These drugs could be used to treat cancer and other genetic disorders.
Research on the spindle apparatus is a rapidly growing field. Scientists are making new discoveries about the spindle apparatus all the time. This research is leading to a better understanding of cell division and the development of new treatments for genetic disorders and cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions About "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle"
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. It is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
Question 1: What is the spindle apparatus?
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division.
Question 2: What are the components of the spindle apparatus?
The spindle apparatus is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins.
Question 3: What is the function of the spindle apparatus?
The function of the spindle apparatus is to move the chromosomes during cell division.
Question 4: How is the spindle apparatus regulated?
The spindle apparatus is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle and the presence of DNA damage.
Question 5: What are the consequences of defects in the spindle apparatus?
Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer.
Question 6: What is the importance of research on the spindle apparatus?
Research on the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer. Research on the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
Transition to the next article section:
The spindle apparatus is a complex and fascinating structure. Scientists are still learning about how the spindle apparatus works and how it is regulated. Research on the spindle apparatus is leading to a better understanding of cell division and the development of new treatments for genetic disorders and cancer.
Tips on "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle"
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. It is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
Tip 1: Understand the structure of the spindle apparatus.
The spindle apparatus is a complex structure that is composed of microtubules, motor proteins, and other proteins. The microtubules are long, thin fibers that extend from one pole of the cell to the other. The motor proteins are responsible for moving the chromosomes along the microtubules. The other proteins help to organize the spindle apparatus and to ensure that the chromosomes are moved correctly.
Tip 2: Understand the function of the spindle apparatus.
The spindle apparatus is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division. It ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Tip 3: Understand the regulation of the spindle apparatus.
The spindle apparatus is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle and the presence of DNA damage.
Tip 4: Understand the consequences of defects in the spindle apparatus.
Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer.
Tip 5: Understand the importance of research on the spindle apparatus.
Research on the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By understanding the spindle apparatus, we can better understand the process of cell division. This knowledge can lead to the development of new treatments for genetic disorders and cancer.
Transition to the article's conclusion:
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer. Research on the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
Conclusion
The spindle apparatus is a critical structure for cell division. It is responsible for moving the chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Defects in the spindle apparatus can lead to a variety of genetic disorders, including aneuploidy and cancer.
Research on the spindle apparatus is important for understanding the causes of genetic disorders and cancer. This research can lead to the development of new treatments for these diseases.
Unlocking Success: Hailey Van Lith's Height And Weight Advantage In Basketball
The Enduring Bond: A Peek Into Andrea Riseborough's Relationship
Uncover Kanye West's Weight: The Definitive Answer