The Ultimate Guide To Mastering The Sum Rule For Derivatives
In mathematics, what is the sum rule for derivatives?
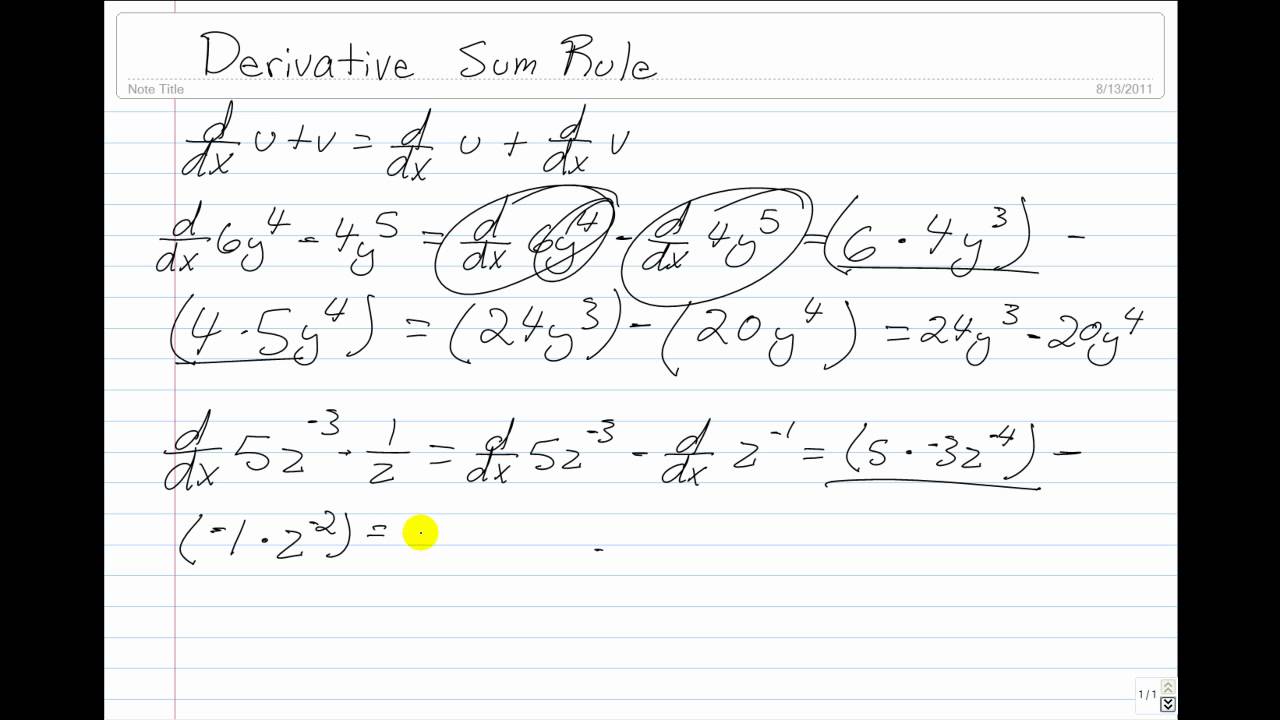
The sum rule for derivatives is a fundamental rule in calculus that allows us to find the derivative of a sum of two or more functions. It states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. That is, if we have two functions f(x) and g(x), then the sum rule for derivatives states that:
(f(x) + g(x))' = f'(x) + g'(x)
This rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions. For example, if we want to find the derivative of the function h(x) = x^2 + sin(x), we can use the sum rule to break it down into the simpler functions f(x) = x^2 and g(x) = sin(x). Then, we can use the power rule and the chain rule to find the derivatives of f(x) and g(x), respectively:
f'(x) = 2x
g'(x) = cos(x)
Finally, we can use the sum rule to combine these derivatives to find the derivative of h(x):
h'(x) = f'(x) + g'(x) = 2x + cos(x)
The sum rule for derivatives is a powerful tool that can be used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions. It is an essential tool for any student of calculus.
Transition to main article topics:
In this article, we will explore the sum rule for derivatives in more detail. We will discuss its importance, its benefits, and its historical context. We will also provide some examples of how to use the sum rule to find the derivatives of complex functions.
The Sum Rule for Derivatives
The sum rule for derivatives is a fundamental rule in calculus that allows us to find the derivative of a sum of two or more functions. It states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. This rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions.
- Simplifies complex functions: The sum rule allows us to break down complex functions into simpler functions, making it easier to find their derivatives.
- Essential for calculus: The sum rule is an essential tool for any student of calculus, as it is used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions.
- Used in real-world applications: The sum rule is used in a variety of real-world applications, such as physics and engineering.
- Historically significant: The sum rule was first discovered by Isaac Newton in the 17th century.
- Easy to apply: The sum rule is a simple and easy-to-apply rule that can be used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions.
The sum rule for derivatives is a powerful tool that can be used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions. It is an essential tool for any student of calculus and is used in a variety of real-world applications.
Example:
Find the derivative of the function f(x) = x^2 + sin(x).
Using the sum rule, we can break this function down into the simpler functions f(x) = x^2 and g(x) = sin(x). Then, we can use the power rule and the chain rule to find the derivatives of f(x) and g(x), respectively:
f'(x) = 2x
g'(x) = cos(x)
Finally, we can use the sum rule to combine these derivatives to find the derivative of h(x):
h'(x) = f'(x) + g'(x) = 2x + cos(x)
Simplifies complex functions
The sum rule for derivatives is a powerful tool that allows us to find the derivatives of complex functions by breaking them down into simpler functions. This is important because it allows us to find the derivatives of functions that would be difficult or impossible to differentiate using other methods.
For example, consider the function f(x) = x^3 + sin(x) + e^x. Using the sum rule, we can break this function down into the simpler functions f(x) = x^3, g(x) = sin(x), and h(x) = e^x. Then, we can use the power rule, the chain rule, and the exponential rule to find the derivatives of f(x), g(x), and h(x), respectively:
f'(x) = 3x^2
g'(x) = cos(x)
h'(x) = e^x
Finally, we can use the sum rule to combine these derivatives to find the derivative of f(x):f'(x) = f'(x) + g'(x) + h'(x) = 3x^2 + cos(x) + e^x
This example shows how the sum rule can be used to simplify the process of finding the derivative of a complex function. By breaking the function down into simpler functions, we can use the power rule, the chain rule, and the exponential rule to find the derivatives of each function individually. Then, we can use the sum rule to combine these derivatives to find the derivative of the original function.The sum rule for derivatives is an essential tool for any student of calculus. It is used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions, including polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions. The sum rule is also used in a variety of real-world applications, such as physics and engineering.
In summary, the sum rule for derivatives is a powerful tool that allows us to find the derivatives of complex functions by breaking them down into simpler functions. This is important because it allows us to find the derivatives of functions that would be difficult or impossible to differentiate using other methods.
Essential for calculus
The sum rule for derivatives is an essential tool for any student of calculus because it allows us to find the derivatives of complex functions by breaking them down into simpler functions. This is important because it allows us to find the derivatives of functions that would be difficult or impossible to differentiate using other methods.
- Simplifies complex functions: The sum rule allows us to break down complex functions into simpler functions, making it easier to find their derivatives.
- Essential for differentiation: The sum rule is essential for finding the derivatives of a wide variety of functions, including polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions.
- Used in real-world applications: The sum rule is used in a variety of real-world applications, such as physics and engineering.
In summary, the sum rule for derivatives is an essential tool for any student of calculus. It is used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions, including complex functions that would be difficult or impossible to differentiate using other methods. The sum rule is also used in a variety of real-world applications.
Used in real-world applications
The sum rule for derivatives is used in a variety of real-world applications because it allows us to find the derivatives of complex functions that are used to model real-world phenomena. For example, the sum rule is used in physics to find the derivatives of functions that describe the motion of objects, and in engineering to find the derivatives of functions that describe the behavior of structures.
One example of how the sum rule is used in physics is in the study of projectile motion. The trajectory of a projectile is described by the function f(x) = -0.5 gx^2 + v x + h, where g is the acceleration due to gravity, v is the initial velocity of the projectile, and h is the initial height of the projectile. The derivative of this function, f'(x) = -gx + v, gives the velocity of the projectile at any point in its trajectory. This information can be used to determine the range of the projectile, the maximum height of the projectile, and the time it takes the projectile to reach its maximum height.
Another example of how the sum rule is used in engineering is in the design of bridges. The load-bearing capacity of a bridge is determined by the function f(x) = P L/8 - Mx^2/2, where P is the total load on the bridge, L is the length of the bridge, M is the mass of the bridge, and x is the distance from the center of the bridge. The derivative of this function, f'(x) = -M*x, gives the shear force at any point in the bridge. This information can be used to determine the maximum shear force that the bridge can withstand, and to design the bridge accordingly.
These are just two examples of how the sum rule for derivatives is used in real-world applications. The sum rule is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a wide variety of problems in physics and engineering.
Historically significant
The sum rule for derivatives is a fundamental rule in calculus that allows us to find the derivative of a sum of two or more functions. It states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. This rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions.
The sum rule was first discovered by Isaac Newton in the 17th century. Newton was one of the greatest mathematicians of all time, and his discovery of the sum rule was a major breakthrough in the development of calculus. The sum rule is now an essential tool for any student of calculus, and it is used in a wide variety of applications, including physics and engineering.
One example of how the sum rule is used in physics is in the study of projectile motion. The trajectory of a projectile is described by the function f(x) = -0.5 gx^2 + v x + h, where g is the acceleration due to gravity, v is the initial velocity of the projectile, and h is the initial height of the projectile. The derivative of this function, f'(x) = -gx + v, gives the velocity of the projectile at any point in its trajectory. This information can be used to determine the range of the projectile, the maximum height of the projectile, and the time it takes the projectile to reach its maximum height.
Another example of how the sum rule is used in engineering is in the design of bridges. The load-bearing capacity of a bridge is determined by the function f(x) = P L/8 - Mx^2/2, where P is the total load on the bridge, L is the length of the bridge, M is the mass of the bridge, and x is the distance from the center of the bridge. The derivative of this function, f'(x) = -M*x, gives the shear force at any point in the bridge. This information can be used to determine the maximum shear force that the bridge can withstand, and to design the bridge accordingly.
These are just two examples of how the sum rule for derivatives is used in real-world applications. The sum rule is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a wide variety of problems in physics and engineering.
Easy to apply
The sum rule for derivatives is a fundamental rule in calculus that allows us to find the derivative of a sum of two or more functions. It states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. This rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions.
- Simplicity and accessibility: The sum rule is a simple and easy-to-understand rule that can be applied to a wide variety of functions. This makes it an accessible tool for students and practitioners alike.
- Broad applicability: The sum rule can be used to find the derivatives of polynomials, trigonometric functions, exponential functions, and logarithmic functions. This makes it a versatile tool that can be used to solve a wide variety of problems.
- Efficiency: The sum rule can often be used to find the derivative of a complex function more quickly and easily than other methods. This makes it a valuable tool for solving problems in physics, engineering, and other fields.
In summary, the sum rule for derivatives is a simple, easy-to-apply rule that can be used to find the derivatives of a wide variety of functions. This makes it a valuable tool for students, practitioners, and anyone else who needs to find the derivative of a function.
FAQs about the Sum Rule for Derivatives
The sum rule for derivatives is a fundamental rule in calculus that allows us to find the derivative of a sum of two or more functions. It states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. This rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the sum rule for derivatives:
Question 1: What is the sum rule for derivatives?The sum rule for derivatives states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. That is, if we have two functions f(x) and g(x), then the sum rule for derivatives states that:
(f(x) + g(x))' = f'(x) + g'(x)
Question 2: Why is the sum rule for derivatives important?
The sum rule for derivatives is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions. This is especially useful for functions that are defined by multiple operations, such as polynomials, trigonometric functions, and exponential functions.
Question 3: How do I use the sum rule for derivatives?
To use the sum rule for derivatives, simply take the derivative of each function in the sum and then add the results. For example, if we have the function f(x) = x^2 + sin(x), we can use the sum rule to find the derivative as follows:
f'(x) = (x^2)' + (sin(x))'
f'(x) = 2x + cos(x)
Question 4: What are some examples of the sum rule for derivatives?
Here are some examples of the sum rule for derivatives:
- (x^2 + sin(x))' = 2x + cos(x)
- (e^x + ln(x))' = e^x + 1/x
- (cos(x) + tan(x))' = -sin(x) + sec^2(x)
Question 5: What are some applications of the sum rule for derivatives?
The sum rule for derivatives is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Finding the velocity and acceleration of an object in motion
- Calculating the rate of change of a function
- Solving optimization problems
Question 6: What are some common misconceptions about the sum rule for derivatives?
One common misconception about the sum rule for derivatives is that it only applies to polynomials. However, the sum rule applies to any function that is defined by a sum of two or more functions.
Another common misconception is that the sum rule for derivatives is difficult to use. However, the sum rule is actually a very simple and straightforward rule to apply.
Summary of key takeaways:
- The sum rule for derivatives states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function.
- The sum rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions.
- The sum rule is easy to use and can be applied to any function that is defined by a sum of two or more functions.
Transition to the next article section:
In the next section, we will discuss the product rule for derivatives.
Conclusion
The sum rule for derivatives is a fundamental rule in calculus that allows us to find the derivative of a sum of two or more functions. It states that the derivative of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the derivatives of each function. This rule is important because it allows us to find the derivative of a complex function by breaking it down into simpler functions.
In this article, we have explored the sum rule for derivatives in detail. We have discussed its importance, its benefits, and its historical context. We have also provided some examples of how to use the sum rule to find the derivatives of complex functions.
The sum rule for derivatives is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a wide variety of problems in physics, engineering, and other fields. It is an essential tool for any student of calculus and a valuable resource for anyone who needs to find the derivative of a function.
Ultimate Guide To Irregular Verbs In French
The Ultimate Guide To Tabasco Sauce: Unlocking Its Scoville Heat Rating
The Ultimate Guide To Vampire Tipsy: Can Vampires Get Drunk?