Unveiling The Literary Currents Of The 20th Century: An In-Depth Exploration
What is 20th Century French Literary Movement and how did it evolve?
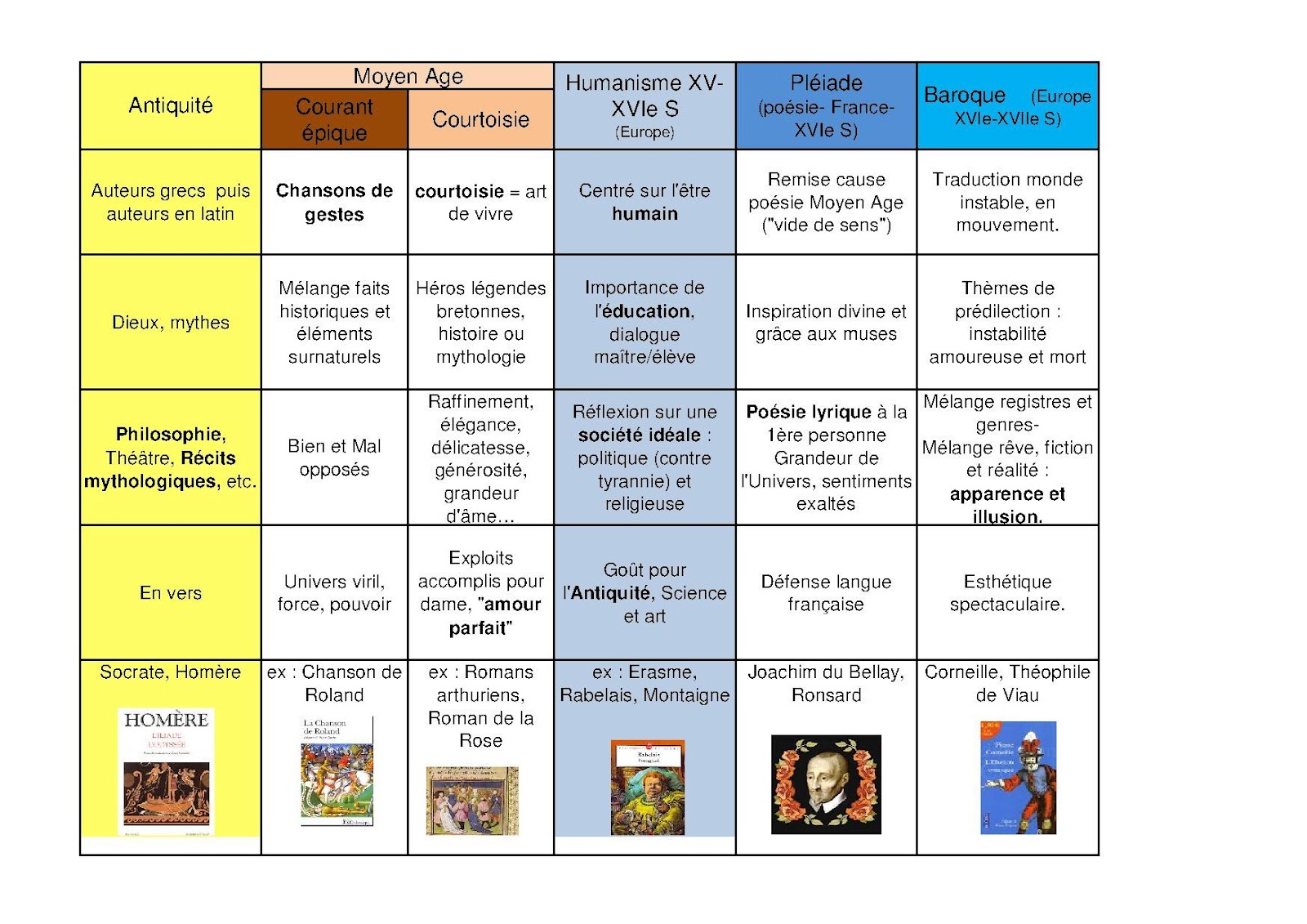
The 20th century was a period of great literary change and innovation in France. This was due in part to the rise of new technologies, such as the printing press, which made it possible to produce and distribute books more widely than ever before. It was also a time of great social and political upheaval, which led to new ways of thinking about the world and human experience.
Some of the most important 20th century French literary movements include:
- Symbolism: This movement, which began in the late 19th century, emphasized the use of symbols to represent inner emotions and experiences. Some of the most famous symbolist writers include Stphane Mallarm, Paul Verlaine, and Arthur Rimbaud.
- Surrealism: This movement, which emerged in the 1920s, sought to explore the unconscious mind and the irrational. Some of the most famous surrealist writers include Andr Breton, Louis Aragon, and Salvador Dal.
- Existentialism: This movement, which emerged in the 1940s, focused on the human condition and the search for meaning in a meaningless world. Some of the most famous existentialist writers include Jean-Paul Sartre, Albert Camus, and Simone de Beauvoir.
These are just a few of the many important literary movements that emerged in France during the 20th century. These movements had a profound impact on the development of French literature and continue to influence writers today.
20th Century French Literary Movements
20th century French literary movements were pivotal in shaping the landscape of modern literature. Here are five key aspects that highlight their significance:
- Symbolism: Explored inner emotions through symbols.
- Surrealism: Delved into the subconscious and irrational.
- Existentialism: Examined the human condition and search for meaning.
- Modernism: Emphasized experimentation and breaking from traditional forms.
- Post-Structuralism: Deconstructed traditional notions of literature and meaning.
These movements not only revolutionized French literature but also influenced global literary thought. Symbolism, with its focus on the evocative power of symbols, paved the way for modernist poetry. Surrealism's exploration of the irrational and subconscious opened up new avenues for artistic expression. Existentialism's examination of human existence resonated deeply with post-war audiences. Modernism's emphasis on experimentation and innovation challenged traditional literary conventions. Post-Structuralism's deconstruction of meaning and language laid the groundwork for contemporary literary theory.
Symbolism
Symbolism emerged as a significant movement within the broader context of 20th century French literary movements ("mouvement littraire au 20e sicle"). This avant-garde approach to literature prioritized the use of symbols to represent and evoke inner emotions and experiences, marking a departure from traditional literary styles.
- Emotive Expression
Symbolist writers employed symbols to convey emotions that defied straightforward description. These symbols often possessed multiple layers of meaning, inviting readers to interpret and engage with the text on a deeper level.
- Subjective Interpretation
Symbolism allowed for a more subjective and personal interpretation of literature. By using symbols, writers could express emotions and ideas that might otherwise be difficult to articulate directly.
- Artistic License
The use of symbols provided writers with greater artistic freedom. They could experiment with language and imagery, creating evocative and suggestive works that transcended the limitations of conventional expression.
- Influence on Modernism
Symbolism's emphasis on subjective experience and experimentation paved the way for the development of modernism in literature. It challenged traditional notions of form and content, encouraging writers to explore new modes of expression.
In conclusion, symbolism played a pivotal role within the broader tapestry of 20th century French literary movements. Its focus on expressing inner emotions through symbols not only transformed the literary landscape of the time but also laid the groundwork for subsequent literary developments.
Surrealism
Surrealism, an influential movement within "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle," emerged as a radical departure from traditional literary norms. This avant-garde approach sought to explore the realms of the subconscious mind and the irrational, challenging conventional notions of reality and artistic expression.
- Unleashing the Unconscious
Surrealists embraced the power of the subconscious, believing it held untapped creative potential. They employed techniques such as automatic writing and dream analysis to bypass conscious control and access the raw, unfiltered thoughts and emotions of the mind.
- Blurring Reality and Imagination
Surrealism sought to dissolve the boundaries between reality and imagination. Writers and artists juxtaposed disparate elements, creating dreamlike and disorienting works that challenged traditional notions of logic and coherence.
- Exploring the Irrational
Surrealists celebrated the irrational and illogical, seeing it as a source of creativity and liberation. They embraced the absurd, the nonsensical, and the bizarre, finding beauty and meaning in the unconventional.
- Influence on Modernism and Beyond
Surrealism's exploration of the subconscious and the irrational had a profound impact on the development of modernism and subsequent literary movements. It challenged traditional narrative structures, opened new avenues for artistic expression, and influenced everything from painting and photography to film and theater.
In conclusion, surrealism's delve into the subconscious and the irrational revolutionized the literary landscape of the 20th century. By embracing the power of the unconscious, blurring the lines between reality and imagination, and celebrating the irrational, surrealism expanded the boundaries of artistic expression and left an indelible mark on modern literature.
Existentialism
Existentialism emerged as a significant philosophical and literary movement within the broader context of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle." This philosophical current profoundly influenced the literary landscape of the 20th century, shaping the themes, perspectives, and artistic expressions of numerous writers and intellectuals.
At the core of existentialism lies the examination of the human condition and the inherent search for meaning in a seemingly absurd and indifferent universe. Existentialist writers explored the themes of individual freedom, responsibility, and the significance of human existence in the face of an often incomprehensible world.
One of the key figures associated with existentialism is the French philosopher and writer Jean-Paul Sartre. In his seminal work, "Nausea," Sartre portrays the existential angst and disillusionment of an individual grappling with the meaninglessness of existence. Similarly, Albert Camus, another prominent existentialist writer, delved into the themes of absurdity, revolt, and the search for meaning in a world devoid of inherent purpose.
The influence of existentialism extended beyond the realm of literature, impacting various disciplines such as philosophy, psychology, and art. It challenged traditional notions of objective truth and morality, emphasizing instead the subjective experiences and choices of individuals.
In conclusion, the connection between existentialism and "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" is undeniable. Existentialism provided a philosophical framework that resonated deeply with the writers and intellectuals of the time, shaping their perspectives on the human condition and the search for meaning in a rapidly changing and often chaotic world.
Modernism
Within the broader context of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle," modernism emerged as a revolutionary force that challenged conventional literary norms and pushed the boundaries of artistic expression. Modernist writers sought to break free from traditional forms and experiment with innovative techniques, perspectives, and styles.
- Stream-of-Consciousness Narration
Modernist writers employed stream-of-consciousness narration to delve into the inner thoughts and emotions of their characters. This technique allowed for a more authentic and nuanced exploration of the human psyche, breaking away from the linear, third-person narratives of the past.
- Fragmentation and Discontinuity
Modernism embraced fragmentation and discontinuity in both form and content. Writers juxtaposed disparate images, ideas, and perspectives, creating a sense of disorientation and challenging traditional notions of coherence and unity.
- Experimental Language and Syntax
Modernist writers experimented with language and syntax, pushing the boundaries of grammar and vocabulary. They employed unconventional punctuation, colloquialisms, and fragmented sentences to create a unique and challenging reading experience.
- Subjectivity and Individualism
Modernism emphasized the subjective experiences and perspectives of individuals. Writers explored the complexities of human consciousness, questioning objective truths and embracing the fluidity of reality.
In conclusion, modernism's emphasis on experimentation and breaking from traditional forms had a profound impact on the evolution of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle." It challenged conventional literary practices, opened up new avenues for artistic expression, and left a lasting legacy in the world of literature.
Post-Structuralism
Post-structuralism emerged as a critical and philosophical movement within the broader context of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle." It challenged the traditional notions of literature and meaning, emphasizing the instability and fluidity of language and the constructed nature of reality.
Post-structuralist thinkers, such as Jacques Derrida and Michel Foucault, argued that there is no single, objective meaning to a text. Instead, meaning is created through the interplay of language, culture, and the reader's own experiences and biases. They also questioned the traditional binary oppositions that had structured Western thought, such as the distinctions between subject and object, truth and falsehood, and presence and absence.
The influence of post-structuralism on "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" is undeniable. It led to a new wave of literary criticism that focused on deconstructing texts and exposing the hidden assumptions and power structures that shape them. Post-structuralist ideas also influenced the work of many creative writers, who experimented with new forms of narrative and challenged traditional notions of authorship and authority.
In conclusion, post-structuralism played a pivotal role in the development of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle." Its emphasis on the deconstruction of traditional notions of literature and meaning opened up new avenues for literary criticism and creative expression, and continues to influence contemporary literary theory and practice.
Frequently Asked Questions about "Mouvement Littraire au 20e Sicle"
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions regarding "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle", providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What is "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle"?
Answer: "Mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" refers to the various literary movements that emerged in France during the 20th century, characterized by their innovative approaches to form, style, and subject matter.
Question 2: What are some of the key movements within "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle"?
Answer: Some prominent movements include Symbolism, Surrealism, Existentialism, Modernism, and Post-Structuralism, each with its distinct characteristics and contributions to French literature.
Question 3: How did "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" impact French literature?
Answer: These movements revolutionized French literature by challenging traditional forms, exploring new themes, and experimenting with language and narrative techniques, leaving a lasting legacy on literary expression.
Question 4: What are some of the common characteristics of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle"?
Answer: Common characteristics include a focus on subjectivity, experimentation, the exploration of the unconscious, and a questioning of traditional notions of reality and meaning.
Question 5: How does "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" relate to other literary movements?
Answer: "Mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" is part of a broader context of literary modernism, influencing and being influenced by contemporary movements in other countries and languages.
Question 6: What is the significance of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle"?
Answer: "Mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" represents a pivotal period in literary history, characterized by its groundbreaking innovations and profound impact on the development of modern literature.
These FAQs provide a glimpse into the multifaceted nature of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" and its enduring legacy in the world of literature.
Transition to the next article section:
For further exploration, the following section delves into the historical and cultural context of "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle", examining its origins, influences, and key figures.
Conclusion
The "mouvement littraire au 20e sicle" was a transformative period in literary history, characterized by a succession of groundbreaking movements that revolutionized the art of writing. From Symbolism's evocative use of symbols to Surrealism's exploration of the subconscious, and from Existentialism's focus on human existence to Modernism's experimentation with form, each movement left an indelible mark on the literary landscape.
These movements not only challenged traditional notions of literature but also reflected the profound social, political, and philosophical changes of the 20th century. They pushed the boundaries of language, narrative, and subject matter, expanding the possibilities of literary expression and paving the way for contemporary literature's diverse and dynamic landscape.
Discover Your Live Account: Unlocking Your Microsoft Portal
The Ultimate Guide To Different Types Of Languages
Is Kirkland Honey Authentic? The Truth Unveiled