The Most Common Surnames In The World: A Comprehensive Guide
What is the most common surname in the world? It's a question that has fascinated genealogists and linguists for centuries. The answer, however, is not as straightforward as one might think.
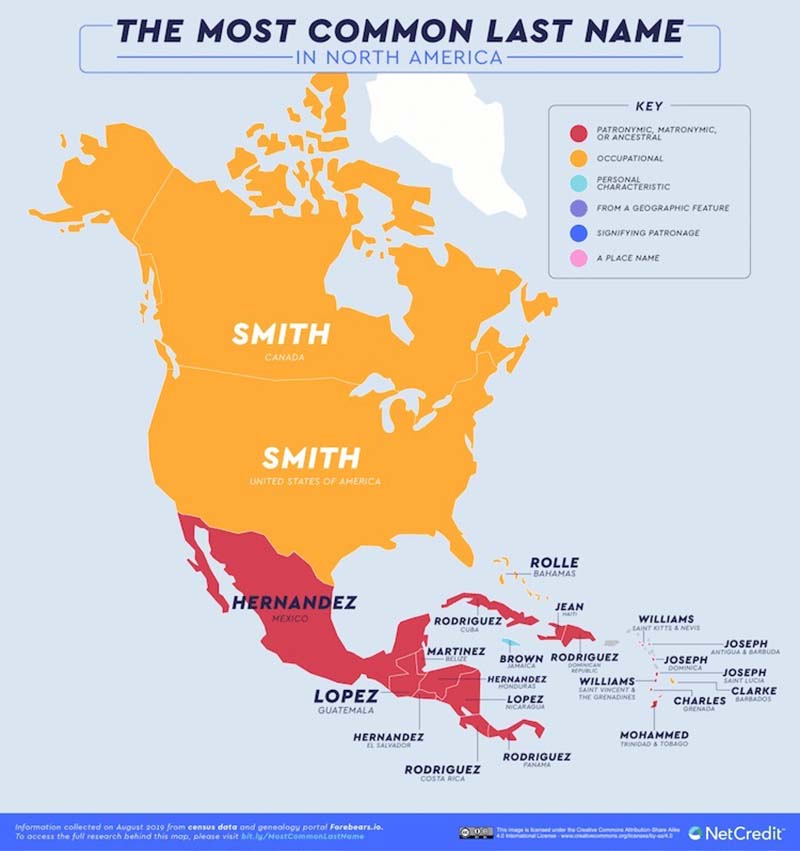
The most common surname in the world is Smith, which is found in many English-speaking countries. Other common surnames include Johnson, Williams, Jones, Brown, Davis, Miller, Wilson, Taylor, and Anderson. These surnames are all of English origin, and they reflect the history of English-speaking peoples around the world.
The importance of surnames cannot be overstated. They provide us with a sense of identity and belonging, and they can tell us a lot about our ancestry. Surnames can also be a source of pride, and they can be passed down from generation to generation.
The study of surnames is a fascinating field, and it can tell us a lot about our past. If you're interested in learning more about your own surname, there are many resources available online and in libraries.
Most Common Surnames in the World
Surnames, an integral part of personal identity, have a rich history and diverse origins. Their prevalence and distribution provide insights into cultural, linguistic, and genealogical patterns across the globe. Here are six key aspects that explore the significance of the most common surnames in the world:
- Global Distribution: Surnames like Smith, Johnson, and Williams transcend national borders, reflecting historical migrations and the spread of dominant cultures.
- Cultural Identity: Surnames often carry cultural connotations, such as Irish (O'Brien), Chinese (Li), or Indian (Singh), serving as markers of ethnic heritage.
- Linguistic Diversity: The origins of surnames reveal linguistic influences, from patronymic naming (e.g., Peterson, son of Peter) to occupational surnames (e.g., Smith, Carpenter).
- Historical Significance: Surnames can trace lineage back to medieval times, providing clues about ancestry and social status.
- Social Stratification: In some cultures, certain surnames have been associated with nobility or elite social classes, reflecting historical power structures.
- Genealogical Research: Surnames are invaluable tools for genealogists, enabling them to trace family histories and uncover connections across generations.
These aspects highlight the multifaceted nature of surnames, from their global distribution to their in shaping personal, cultural, and historical narratives.
Global Distribution
The global distribution of common surnames is a testament to the interconnectedness of human history. Surnames like Smith, Johnson, and Williams are found in many countries around the world, reflecting the historical migrations and spread of dominant cultures.
For example, the surname Smith is the most common surname in England, the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. This is due to the historical dominance of English culture in these countries. Similarly, the surname Johnson is the most common surname in Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Finland. This is due to the historical dominance of Scandinavian culture in these countries.
The global distribution of common surnames is a reminder of the interconnectedness of human history. It is also a reminder of the importance of cultural diversity. The different surnames that we have today reflect the rich tapestry of human history.
Cultural Identity
Surnames are not just identifiers; they carry cultural connotations that reflect the ethnic heritage of individuals. This connection is particularly evident among the most common surnames in the world.
- Patronymic Surnames: Many common surnames originated as patronymic surnames, meaning they were derived from the father's name. For example, the surname Johnson is derived from the given name John, and the surname O'Brien is derived from the Irish given name Brian.
- Occupational Surnames: Other common surnames originated as occupational surnames, meaning they were derived from the occupation of the individual's ancestor. For example, the surname Smith is derived from the occupation of blacksmith, and the surname Carpenter is derived from the occupation of carpenter.
- Geographical Surnames: Some common surnames originated as geographical surnames, meaning they were derived from the place where the individual's ancestor lived. For example, the surname Hill is derived from the Old English word for "hill," and the surname Forest is derived from the Old French word for "forest."
- Cultural Surnames: Finally, some common surnames originated as cultural surnames, meaning they were derived from cultural or religious beliefs. For example, the surname Cohen is derived from the Hebrew word for "priest," and the surname Singh is derived from the Sikh word for "lion."
The connection between surnames and cultural identity is undeniable. Surnames can tell us a lot about a person's ancestry, heritage, and culture. They can also serve as a source of pride and identity.
Linguistic Diversity
The linguistic diversity of surnames is a reflection of the diverse linguistic heritage of human populations. Surnames can provide insights into the languages spoken by our ancestors and the cultural and social practices of the societies in which they lived.
- Patronymic Surnames: Patronymic surnames are derived from the father's name, indicating a person's lineage. This type of surname is common in many cultures around the world, including English, Scandinavian, Slavic, and Arabic cultures. For example, the surname Johnson is derived from the given name John, and the surname Patel is derived from the given name Peter.
- Occupational Surnames: Occupational surnames are derived from the occupation of the individual's ancestor. This type of surname is common in many cultures around the world, including English, French, German, and Chinese cultures. For example, the surname Smith is derived from the occupation of blacksmith, and the surname Carpenter is derived from the occupation of carpenter.
- Geographical Surnames: Geographical surnames are derived from the place where the individual's ancestor lived. This type of surname is common in many cultures around the world, including English, French, Spanish, and Chinese cultures. For example, the surname Hill is derived from the Old English word for "hill," and the surname Forest is derived from the Old French word for "forest."
- Cultural Surnames: Cultural surnames are derived from cultural or religious beliefs. This type of surname is common in many cultures around the world, including Jewish, Muslim, and Hindu cultures. For example, the surname Cohen is derived from the Hebrew word for "priest," and the surname Singh is derived from the Sikh word for "lion."
The linguistic diversity of surnames is a reminder of the rich tapestry of human history. Surnames can tell us a lot about our ancestors, their culture, and their way of life.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of surnames lies in their ability to trace lineage back to medieval times, offering valuable clues about ancestry and social status. This aspect is particularly relevant to the study of the most common surnames in the world, as they often have deep historical roots and can reveal fascinating insights into the past.
- Lineage and Ancestry: Common surnames like Smith, Johnson, and Williams have been passed down through generations, providing a direct link to one's ancestors. By researching the origin and distribution of these surnames, individuals can gain insights into their family history and trace their lineage back to specific regions or time periods.
- Social Status and Nobility: In many cultures, certain surnames have been associated with nobility or elite social classes. For example, the surname "de" in French surnames often indicates aristocratic lineage, while the surname "von" in German surnames suggests nobility. Studying the historical context of common surnames can shed light on the social stratification and power structures of past societies.
- Occupational Origins: Many common surnames originated from occupations held by ancestors. For instance, the surname "Cooper" indicates a lineage of barrel makers, while the surname "Shepherd" suggests ancestors who were shepherds. These surnames provide glimpses into the livelihoods and economic activities of past generations.
- Geographical Origins: Common surnames can also reveal geographical origins. Surnames like "Hill" or "Forest" may indicate that ancestors lived in areas with those topographical features. Studying the distribution of surnames across different regions can provide insights into migration patterns and historical settlement patterns.
In conclusion, the historical significance of surnames is intertwined with the study of the most common surnames in the world. By delving into the origins and evolution of these surnames, we gain valuable insights into our ancestry, social history, and the cultural tapestry of human civilization.
Social Stratification
The connection between social stratification and the most common surnames in the world lies in the historical power structures that have influenced the distribution and significance of surnames. In many cultures, certain surnames have been associated with nobility or elite social classes, reflecting the social hierarchies and power dynamics of the time.
- Lineage and Ancestry: Common surnames associated with nobility often indicate lineage and ancestry traced back to aristocratic families or ruling dynasties. For example, in European cultures, surnames like "de" or "von" have historically been associated with noble lineage.
- Land Ownership and Wealth: In agrarian societies, surnames could reflect land ownership and wealth, which were often concentrated among elite families. Surnames derived from, such as "Hill" or "Forest," might indicate that ancestors owned significant property or resided in prestigious areas.
- Occupational Prestige: Certain occupations were held in high regard and associated with elite status. Surnames derived from these occupations, such as "Physician" or "Judge," could indicate ancestors who held respected positions in society.
- Royal Patronage and Grants: Monarchs and rulers often granted surnames or modified existing ones as a mark of favor or reward for loyalty and service. These surnames, often including elements like "Royal" or "Grant," could signify connections to the ruling class.
The presence of these surnames among the most common in the world reflects the enduring influence of social stratification and historical power structures. While societal norms and class systems may have evolved over time, the surnames associated with elite lineages continue to hold significance and provide insights into the social dynamics of the past.
Genealogical Research
In the realm of genealogical research, surnames occupy a central position as indispensable tools for tracing family histories and uncovering connections across generations. The prevalence of certain surnames globally adds another dimension to this significance, allowing genealogists to leverage their frequency and distribution patterns for deeper insights.
- Establishing Ancestry and Lineage:
Common surnames often serve as signposts, guiding genealogists towards potential ancestral lines. By identifying the geographical origins and historical prevalence of these surnames, researchers can narrow down their search and establish connections to specific families or regions.
- Bridging Historical Gaps:
The persistence of common surnames over time enables genealogists to bridge historical gaps and connect individuals across centuries. By tracing the evolution and migration patterns of these surnames, researchers can gain insights into the movements and interactions of families throughout history.
- Uncovering Cultural and Social Context:
Common surnames often reflect cultural and social conventions, providing genealogists with valuable clues about the lives and experiences of their ancestors. For instance, occupational surnames can shed light on family trade traditions, while geographical surnames can indicate ancestral origins and migration patterns.
- Identifying Genetic Connections:
In conjunction with DNA analysis, common surnames can assist in identifying genetic connections between individuals. By establishing shared ancestral surnames, genealogists can corroborate genetic evidence and uncover hidden familial relationships.
The prevalence of certain surnames globally expands the scope of genealogical research, enabling researchers to explore broader patterns of human migration, cultural exchange, and historical events. By harnessing the insights offered by common surnames, genealogists can uncover the rich tapestry of family histories and connect individuals to their ancestors across time and space.
FAQs on Most Common Surnames in the World
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the topic of the most common surnames in the world, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the top 10 most common surnames globally?
Answer: The top 10 most common surnames worldwide are Wang, Li, Zhang, Chen, Liu, Yang, Huang, Zhao, Wu, and Zhou.
Question 2: Why are certain surnames more common than others?
Answer: Surnames become prevalent due to various factors, including population size, historical migrations, cultural practices, and naming conventions.
Question 3: Do common surnames indicate shared ancestry?
Answer: While common surnames may suggest a shared ancestry, it is not always the case. Surnames can be adopted, changed, or shared among unrelated individuals.
Question 4: Can common surnames reveal cultural or geographical origins?
Answer: Yes, some common surnames have cultural or geographical origins, reflecting the language, ethnicity, or region of their bearers.
Question 5: How can I trace my family history using my surname?
Answer: Surnames are valuable tools for genealogical research, providing clues about ancestral origins and connections to specific families or regions.
Question 6: Are there any trends or patterns in the distribution of common surnames?
Answer: Common surnames often exhibit geographical patterns, reflecting historical migrations, settlements, and cultural influences.
Summary: Understanding the most common surnames in the world provides insights into cultural diversity, historical migrations, and the complex tapestry of human history. Surnames serve as valuable tools for genealogical research and can reveal fascinating stories about our ancestors and the societies they lived in.
Transition to the next article section:
Conclusion
Our exploration of the most common surnames in the world has revealed a rich tapestry of human history, cultural diversity, and linguistic influences. These surnames, passed down through generations, carry stories of our ancestors and the societies they lived in.
The study of common surnames is not merely an academic pursuit; it is a journey of self-discovery and a celebration of our shared humanity. By understanding the origins and distribution of our surnames, we gain insights into our past, our present, and our place in the ever-evolving story of humankind.
Understanding Transient Thyroiditis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
When Did Cisneros Begin Crafting Her Literary Works?
Discover The Unparalleled Quality Of Wirbo Plumbing Fittings