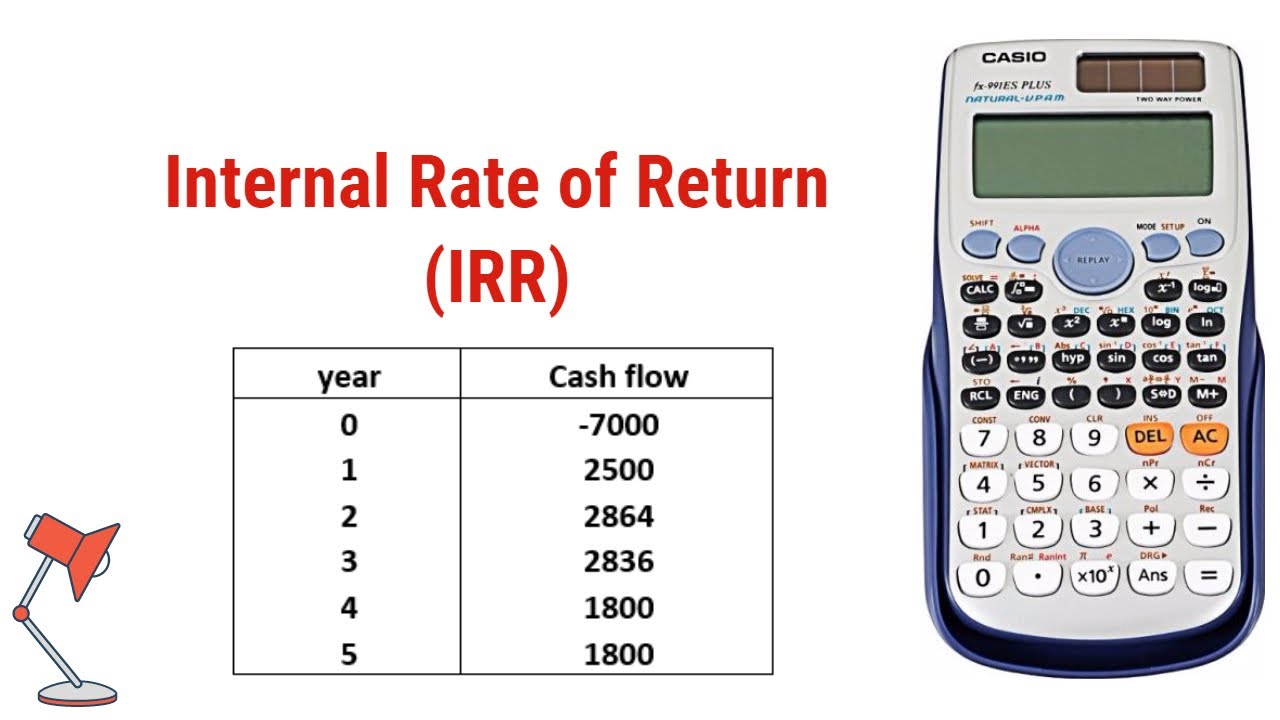
How To Calculate IRR: The Ultimate Guide For Investors
How to Calculate Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a metric used in capital budgeting to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It represents the annualized rate of return that an investment is expected to generate over its lifetime. IRR is a crucial financial tool that helps businesses make informed decisions about which projects to invest in and which to reject.
IRR is calculated by finding the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of an investment equal to zero. NPV is the sum of all the future cash flows of an investment, discounted back to the present day using a given discount rate. If the IRR of an investment is greater than the cost of capital, then the investment is considered to be profitable and should be accepted. Conversely, if the IRR is less than the cost of capital, then the investment should be rejected.
Calculating IRR can be complex, but there are a number of financial calculators and software programs that can be used to simplify the process. Once the IRR has been calculated, it can be used to compare different investment opportunities and to make informed decisions about which projects to pursue.
IRR is a powerful financial tool that can help businesses make better investment decisions. By understanding how to calculate IRR, businesses can increase their chances of making profitable investments and achieving their financial goals.
How to Calculate IRR
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It represents the annualized rate of return that an investment is expected to generate over its lifetime. IRR is a powerful tool that helps businesses make informed decisions about which projects to invest in and which to reject.
- Definition: IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of an investment equal to zero.
- Importance: IRR helps businesses identify profitable investments and make informed capital budgeting decisions.
- Calculation: IRR can be calculated using financial calculators or software programs.
- Comparison: IRR can be used to compare different investment opportunities and select the most profitable ones.
- Limitations: IRR assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR, which may not always be realistic.
- Applications: IRR is widely used in various industries, including finance, real estate, and project management.
In conclusion, IRR is a versatile financial tool that provides valuable insights into the profitability of investments. By understanding the key aspects of IRR, businesses can make better investment decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Definition
The definition of IRR is closely connected to the process of calculating IRR. NPV is a crucial concept in capital budgeting, and it represents the sum of all the future cash flows of an investment, discounted back to the present day using a given discount rate. By setting NPV equal to zero, we can solve for the discount rate that makes the investment neither profitable nor unprofitable. This discount rate is the IRR.
To calculate IRR, we can use a financial calculator or software program. These tools can quickly and easily solve for IRR, even for complex investment scenarios. Once the IRR has been calculated, it can be used to compare different investment opportunities and to make informed decisions about which projects to pursue.
The concept of IRR is essential for making sound investment decisions. By understanding how IRR is calculated and how it can be used, businesses can increase their chances of making profitable investments and achieving their financial goals.
Importance
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It represents the annualized rate of return that an investment is expected to generate over its lifetime. By understanding how to calculate IRR, businesses can make informed decisions about which projects to invest in and which to reject.
- Investment Analysis: IRR helps businesses analyze the potential profitability of different investment opportunities. By comparing the IRR of different projects, businesses can identify the projects that are most likely to generate a positive return on investment.
- Capital Budgeting: IRR is a key tool used in capital budgeting, the process of making investment decisions. By using IRR, businesses can determine which projects are most worthy of their limited capital resources.
- Project Selection: IRR can be used to select the best projects from a pool of potential investments. By choosing projects with a high IRR, businesses can increase their chances of achieving their financial goals.
- Risk Assessment: IRR can also be used to assess the risk of an investment. Projects with a high IRR are generally considered to be less risky than projects with a low IRR.
In conclusion, IRR is a versatile financial tool that provides valuable insights into the profitability and risk of investments. By understanding how to calculate and use IRR, businesses can make better investment decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Calculation
Calculating IRR can be a complex process, especially for investments with uneven cash flows. Financial calculators and software programs simplify this process by automating the calculations and providing accurate results.
- Convenience: Financial calculators and software eliminate the need for manual calculations, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
- Accuracy: These tools use precise algorithms to calculate IRR, ensuring reliable and consistent results.
- Flexibility: Financial calculators and software can handle a wide range of investment scenarios, including complex cash flow patterns and multiple investment periods.
- Additional Features: Many financial calculators and software programs offer additional features, such as NPV calculation, sensitivity analysis, and scenario modeling, which can further support investment analysis.
In conclusion, financial calculators and software programs are powerful tools that make IRR calculations accessible and efficient. By utilizing these tools, businesses can accurately evaluate the profitability of investments and make informed capital budgeting decisions.
Comparison
The comparison of IRRs is a crucial aspect of evaluating investment opportunities. By calculating the IRR of different projects, businesses can identify the projects that are most likely to generate a positive return on investment.
To illustrate, consider two investment opportunities: Project A with an IRR of 12% and Project B with an IRR of 15%. By comparing the IRRs, it is evident that Project B is the more profitable investment. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about which projects to pursue.
The comparison of IRRs is not only limited to two projects. Businesses can compare multiple investment opportunities to select the most profitable ones. This comprehensive analysis ensures that businesses allocate their capital resources to the projects that will generate the highest returns.
In conclusion, the comparison of IRRs is an essential component of the investment evaluation process. By understanding how to calculate and compare IRRs, businesses can make informed decisions and maximize their investment returns.
Limitations
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a widely used metric for evaluating the profitability of investments. However, one of its limitations is the assumption that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR throughout the investment's lifetime. This assumption may not always hold true in, which can lead to inaccuracies in IRR calculations.
- Impact of Reinvestment Rate: The IRR calculation assumes that all cash flows are reinvested at the IRR. However, in reality, the reinvestment rate may vary depending on market conditions, investment opportunities, and the company's financial situation. If the actual reinvestment rate is lower than the IRR, the actual return on investment will be lower than the IRR.
- Changing Investment Environment: The IRR calculation assumes that the investment environment remains constant throughout the investment's lifetime. However, the investment environment can change significantly over time, affecting factors such as interest rates, inflation, and economic conditions. These changes can impact the reinvestment rate and, consequently, the actual return on investment.
- Multiple Investment Options: The IRR calculation does not consider the availability of alternative investment options. In reality, businesses may have multiple investment opportunities with different risk and return profiles. The decision of where to reinvest cash flows should consider these alternatives, which the IRR calculation does not capture.
- Behavioral Factors: The IRR calculation does not account for behavioral factors that may influence the reinvestment decision. For example, managers may be reluctant to reinvest cash flows at the IRR if they are risk-averse or if they have other investment priorities.
In conclusion, while IRR is a useful metric for evaluating investment profitability, its assumption of constant reinvestment at the IRR can lead to inaccuracies. Businesses should be aware of this limitation and consider other factors when making investment decisions.
Applications
The connection between the applications of IRR and the methods for calculating it lies in the fact that the calculation of IRR provides the foundation for understanding its practical applications. IRR is a powerful financial metric that helps businesses make informed investment decisions, and its calculation is essential for leveraging its benefits in various industries.
In finance, IRR is used to evaluate the profitability of investment opportunities such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. By calculating the IRR of different investments, financial analysts can compare and select the ones with the highest potential return. Similarly, in real estate, IRR is used to assess the viability of property investments. Real estate investors use IRR to determine the profitability of purchasing, developing, or renting properties.
Project management professionals also utilize IRR to evaluate the financial feasibility of projects. By calculating the IRR of a project, project managers can determine its potential return on investment and make informed decisions about resource allocation and project selection. IRR helps businesses prioritize projects with higher profitability and make strategic decisions that align with their financial goals.
In conclusion, the calculation of IRR is intricately linked to its applications in various industries. By understanding how to calculate IRR, businesses can harness its power to make informed investment decisions, assess the profitability of projects, and achieve their financial objectives.
FAQs on Calculating Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a crucial financial metric for evaluating the profitability of investments. Here are some frequently asked questions about calculating IRR:
Question 1: What is the formula for calculating IRR?
Answer: IRR is calculated by finding the discount rate that makes the net present value (NPV) of an investment equal to zero. NPV is the sum of all the future cash flows of an investment, discounted back to the present day using a given discount rate.
Question 2: How can I calculate IRR manually?
Answer: Calculating IRR manually can be complex. It involves using a trial-and-error approach to find the discount rate that makes NPV equal to zero. Financial calculators or software programs can simplify this process.
Question 3: What are the limitations of IRR?
Answer: IRR assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR, which may not always be realistic. It also does not consider the risk of an investment.
Question 4: How is IRR used in investment decision-making?
Answer: IRR is used to compare the profitability of different investment opportunities. Investments with a higher IRR are generally considered to be more profitable.
Question 5: What is the difference between IRR and NPV?
Answer: NPV is the sum of all the future cash flows of an investment, discounted back to the present day using a given discount rate. IRR is the discount rate that makes NPV equal to zero.
Question 6: How can I learn more about calculating IRR?
Answer: There are many resources available to learn more about calculating IRR, including books, articles, and online courses.
Calculating IRR is an important skill for anyone involved in investment analysis. By understanding how to calculate IRR, you can make informed investment decisions and achieve your financial goals.
Conclusion
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a critical metric in capital budgeting, providing businesses with a comprehensive understanding of an investment's profitability. This guide has explored the intricacies of calculating IRR, emphasizing its importance and the factors that influence its accuracy.
Accurately calculating IRR is paramount for making sound investment decisions. By considering the limitations and assumptions associated with IRR, businesses can effectively assess the potential returns and risks of various investment opportunities. Moreover, understanding the methodologies for calculating IRR empowers businesses to make informed choices that align with their financial goals and objectives.
The Ultimate Guide To Waldorf Colours Of The Week: Unlocking Creativity And Imagination
Discover Shapes With Adjacently Aligned, Identical Sides
Understanding The Energy Levels Of Sodium: A Comprehensive Guide