Unlocking Energy: A Comprehensive Guide To ATP, The Body's Power Source
What is the primary source of ATP in the human body? The answer is: the mitochondria.
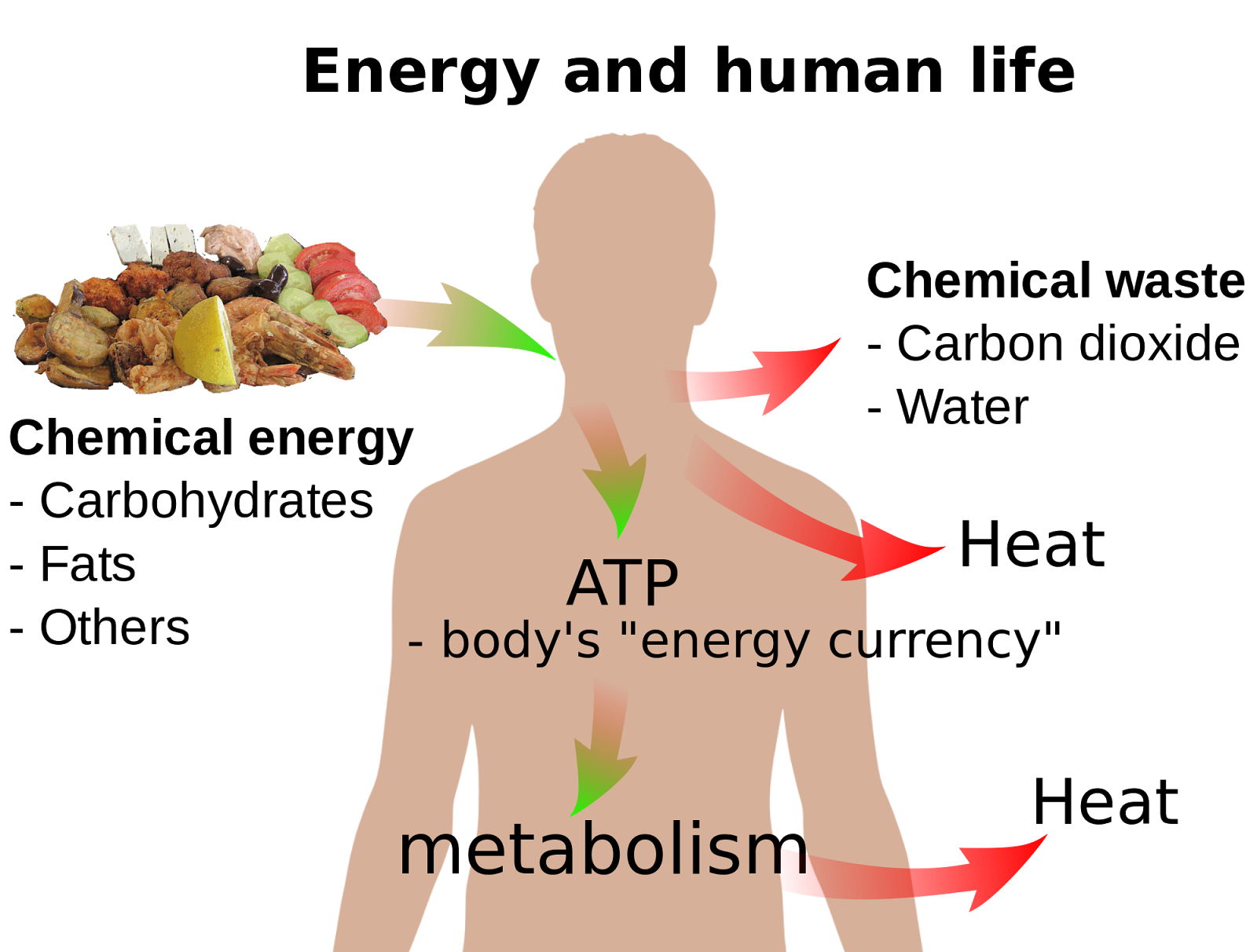
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells, which are small organelles that are responsible for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose into energy.
The mitochondria use a series of chemical reactions to convert glucose into ATP. These reactions take place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria, which is folded into a series of cristae. The cristae increase the surface area of the inner membrane, which allows for more ATP to be produced. ATP is then transported out of the mitochondria and into the cytoplasm, where it can be used by cells for energy.
ATP is essential for a variety of cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly and would eventually die.
The Primary Source for ATP in the Human Body
The primary source of ATP in the human body is the mitochondria. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells, which are small organelles that are responsible for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose into energy.
- Cellular respiration: The process by which cells convert glucose into ATP.
- Mitochondria: The small organelles in cells that are responsible for cellular respiration and ATP production.
- ATP synthase: The enzyme that produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
- ADP: Adenosine diphosphate, the molecule that is converted into ATP by ATP synthase.
- Phosphate: The inorganic molecule that is added to ADP to form ATP.
- Energy: The primary function of ATP, providing energy for cells.
These six key aspects provide a comprehensive overview of the primary source of ATP in the human body. ATP is essential for a variety of cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly and would eventually die.
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the primary process by which cells convert glucose into ATP, the primary source of energy for the human body. Without cellular respiration, cells would not be able to produce ATP, and would eventually die. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells. The mitochondria are small organelles that are responsible for a variety of cellular functions, including ATP production. The process of cellular respiration begins with the breakdown of glucose, a sugar molecule that is obtained from food. Glucose is broken down into pyruvate, which is then converted into acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is then used to produce ATP through a series of chemical reactions. The chemical reactions that take place during cellular respiration are very complex. However, the overall process can be summarized as follows: Glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + ATP The ATP that is produced during cellular respiration is used to power a variety of cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly and would eventually die.
Cellular respiration is a vital process for the human body. It is the primary means by which cells obtain the energy that they need to function. Without cellular respiration, the human body would not be able to survive.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are the primary source of ATP in the human body. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells through a process called cellular respiration.
- Cellular respiration: The process by which cells convert glucose into ATP.
- Mitochondria: The small organelles in cells that are responsible for cellular respiration and ATP production.
- ATP synthase: The enzyme that produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
- ADP: Adenosine diphosphate, the molecule that is converted into ATP by ATP synthase.
- Phosphate: The inorganic molecule that is added to ADP to form ATP.
- Energy: The primary function of ATP, providing energy for cells.
These six key aspects provide a comprehensive overview of the connection between mitochondria and ATP production in the human body. ATP is essential for a variety of cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly and would eventually die.
ATP synthase
ATP synthase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the primary source of ATP in the human body. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells through a process called cellular respiration.
ATP synthase is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. It is a large, complex enzyme that consists of several subunits. The enzyme works by using the energy from a proton gradient to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP. The proton gradient is created by the electron transport chain, which is another enzyme complex located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
ATP synthase is essential for the production of ATP. Without ATP synthase, cells would not be able to produce the energy that they need to function. This would lead to cell death and eventually to the death of the organism.
ATP synthase is a vital enzyme that plays a key role in the primary source of ATP in the human body. It is a complex enzyme that is essential for the production of ATP, the primary source of energy for cells.
ADP
ADP, or adenosine diphosphate, is a molecule that plays a crucial role in the primary source of ATP in the human body. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells through a process called cellular respiration.
- ADP and ATP: ADP is the molecule that is converted into ATP by ATP synthase. ATP synthase is an enzyme that is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. It uses the energy from a proton gradient to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP.
- The role of ADP in cellular respiration: ADP is essential for the production of ATP. Without ADP, ATP synthase would not be able to convert inorganic phosphate into ATP. This would lead to a decrease in the production of ATP and eventually to cell death.
- ADP and energy production: ADP is a key molecule in the production of energy in the human body. It is the molecule that is converted into ATP, which is the primary source of energy for cells.
ADP is a vital molecule that plays a key role in the primary source of ATP in the human body. It is the molecule that is converted into ATP by ATP synthase, which is the enzyme that produces ATP. ADP is essential for the production of ATP, which is the primary source of energy for cells.
Phosphate
Phosphate is an inorganic molecule that plays a crucial role in the primary source of ATP in the human body. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells through a process called cellular respiration.
- The role of phosphate in ATP production: Phosphate is essential for the production of ATP. It is the molecule that is added to ADP to form ATP. This process is carried out by the enzyme ATP synthase, which is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
- The importance of phosphate for cellular function: Phosphate is essential for the function of cells. It is a component of many important molecules, including DNA, RNA, and phospholipids. Phosphate also plays a role in a variety of cellular processes, including energy production, signal transduction, and muscle contraction.
- Phosphate deficiency: Phosphate deficiency can lead to a number of health problems, including muscle weakness, fatigue, and bone pain. In severe cases, phosphate deficiency can be fatal.
Phosphate is a vital molecule that plays a key role in the primary source of ATP in the human body. It is essential for the production of ATP, which is the primary source of energy for cells. Phosphate also plays a role in a variety of other cellular processes, including the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and phospholipids. Phosphate deficiency can lead to a number of health problems, including muscle weakness, fatigue, and bone pain.
Energy
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary source of energy for cells. It is a small molecule that consists of an adenine molecule, a ribose molecule, and three phosphate groups. ATP is produced in the mitochondria of cells through a process called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose into ATP.
ATP is essential for a variety of cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly and would eventually die.
The primary source of ATP in the human body is the mitochondria. Mitochondria are small organelles that are found in the cytoplasm of cells. Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration and the production of ATP. Without mitochondria, cells would not be able to produce ATP and would eventually die.
The connection between "Energy: The primary function of ATP, providing energy for cells" and "the primary source for ATP is the human body is" is clear. ATP is the primary source of energy for cells, and the mitochondria are the primary source of ATP in the human body. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly and would eventually die. Without mitochondria, cells would not be able to produce ATP and would eventually die.
This understanding has a number of practical applications. For example, it can be used to develop new drugs to treat diseases that are caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. It can also be used to develop new ways to improve athletic performance by increasing the production of ATP.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions related to the primary source of ATP in the human body. These questions are answered in a serious and informative tone, providing a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What is the primary source of ATP in the human body?
Answer: The mitochondria are the primary source of ATP in the human body. ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate and is the main energy currency of cells. Mitochondria are small organelles found in the cytoplasm of cells and are responsible for cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert glucose into ATP.
Question 2: Why are mitochondria important for ATP production?
Answer: Mitochondria contain specialized proteins and enzymes necessary for cellular respiration and ATP synthesis. They have folded inner membranes called cristae, which increase surface area for efficient energy production.
Question 3: How is ATP used in the body?
Answer: ATP is the primary energy source for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, protein synthesis, and active transport of molecules across cell membranes.
Question 4: What happens if ATP production is impaired?
Answer: Impaired ATP production can lead to cellular dysfunction and tissue damage. It can contribute to fatigue, muscle weakness, and organ failure in severe cases.
Question 5: Can ATP be produced outside the mitochondria?
Answer: While mitochondria are the primary source of ATP, small amounts of ATP can be produced in the cytoplasm through glycolysis, a process that breaks down glucose without oxygen.
Question 6: How can we support mitochondrial function?
Answer: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can support mitochondrial function and ATP production. Certain vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants have also been linked to mitochondrial health.
Remember, understanding the primary source of ATP in the human body is crucial for appreciating the fundamental energy processes that sustain life.
Transition to the next article section: The Importance of ATP in Cellular Processes
Conclusion
ATP, the primary source of energy for the human body, is primarily produced in the mitochondria, the cellular organelles responsible for cellular respiration. This intricate process underscores the fundamental importance of mitochondria in sustaining life.
Understanding the primary source of ATP provides a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance of cellular processes that maintain homeostasis and support overall health. It highlights the critical role of mitochondria and cellular respiration in ensuring the body's energy requirements are met.
Taylor Kinney's Wife: Uncovering The Truth Behind The Hollywood Heartthrob's Love Life
Unlocking The Power Of Non-Reducing Treatments
Unlock Detroit's Capital Gains Tax Exemption: A Guide To Your Financial Freedom