Essential Examples Of Atoms And Molecules For Enhanced Understanding
What are examples of atoms and molecules?
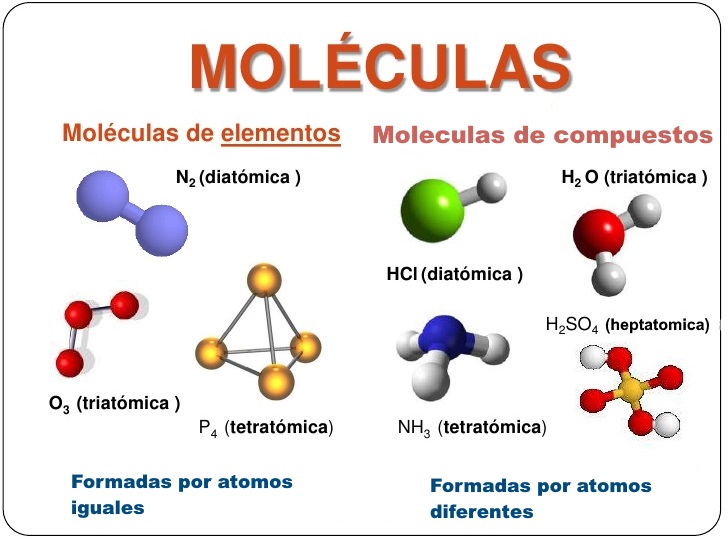
Examples of atoms include hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. Examples of molecules include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4). Atoms are the basic units of matter, while molecules are groups of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
Atoms and molecules are essential to life. Atoms make up everything in the universe, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. Molecules are responsible for the chemical reactions that occur in our bodies and in the world around us.
The study of atoms and molecules is called chemistry. Chemistry is a vast and complex field, but it is essential for understanding the world around us.
Examples of atoms and molecules
Examples of atoms include hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. Examples of molecules include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4). Atoms are the basic units of matter, while molecules are groups of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
- Essential building blocks of matter
- Foundation of chemical reactions
- Key to understanding the universe
- Basis of all physical properties
- Building blocks of life
- Essential for technology and medicine
These key aspects highlight the importance of examples of atoms and molecules in various scientific fields. From the smallest particles of matter to the largest structures in the universe, atoms and molecules are the building blocks of everything. They are essential for life, technology, and medicine. By understanding the properties and behavior of atoms and molecules, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Essential building blocks of matter
Atoms and molecules are the essential building blocks of matter. They are the basic units from which all matter is made, from the smallest particles to the largest structures in the universe. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Molecules are groups of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
- Components
The components of atoms and molecules are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which identifies the element. The number of neutrons determines the isotope of the element.
- Examples
Examples of atoms include hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. Examples of molecules include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4). Atoms are the basic units of matter, while molecules are groups of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
- Implications
Atoms and molecules are the essential building blocks of matter. They determine the physical and chemical properties of all substances. The study of atoms and molecules is called chemistry. Chemistry is a vast and complex field, but it is essential for understanding the world around us.
Atoms and molecules are essential for life. They make up everything in the universe, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. Molecules are responsible for the chemical reactions that occur in our bodies and in the world around us.
Foundation of chemical reactions
Atoms and molecules are the foundation of chemical reactions. Chemical reactions are the processes by which atoms and molecules rearrange themselves to form new substances. These reactions are essential for life, as they allow us to convert food into energy, build new molecules, and eliminate waste products.
- Reactants and products
In a chemical reaction, the atoms and molecules that are present at the beginning of the reaction are called the reactants. The atoms and molecules that are formed at the end of the reaction are called the products. The reactants and products are always different substances.
- Chemical bonds
Chemical reactions involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms and molecules together. There are many different types of chemical bonds, and the type of bond that is formed depends on the atoms involved.
- Energy
Chemical reactions can release or absorb energy. The energy that is released or absorbed is called the heat of reaction. The heat of reaction can be used to do work, such as heating a house or powering a car.
- Examples
Examples of chemical reactions include:
- The burning of wood
- The rusting of iron
- The digestion of food
- The photosynthesis of plants
Atoms and molecules are the essential building blocks of matter, and chemical reactions are the processes by which atoms and molecules rearrange themselves to form new substances. Chemical reactions are essential for life, and they play a role in many different processes, from the burning of wood to the digestion of food.
Key to understanding the universe
Examples of atoms and molecules are key to understanding the universe because they are the basic building blocks of all matter. By studying atoms and molecules, scientists can learn about the composition and structure of the universe, as well as the forces that govern its behavior.
- Components of the universe
Atoms and molecules are the components of all matter, from the smallest particles to the largest structures in the universe. By studying atoms and molecules, scientists can learn about the composition of the universe and how it has evolved over time.
- Forces that govern the universe
Atoms and molecules are governed by the laws of physics and chemistry. By studying atoms and molecules, scientists can learn about the forces that govern the universe and how they interact with each other.
- Origin and evolution of the universe
Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of stars and planets. By studying atoms and molecules, scientists can learn about the origin and evolution of the universe.
In conclusion, examples of atoms and molecules are key to understanding the universe because they are the basic building blocks of all matter. By studying atoms and molecules, scientists can learn about the composition and structure of the universe, as well as the forces that govern its behavior.
Basis of all physical properties
Examples of atoms and molecules are the basis of all physical properties. The physical properties of a substance are the properties that can be observed without changing the substance's chemical composition. These properties include things like color, density, melting point, and boiling point.
The physical properties of a substance are determined by the atoms and molecules that make up the substance. For example, the density of a substance is determined by the mass of the atoms and molecules in a given volume of the substance. The melting point of a substance is determined by the strength of the bonds between the atoms and molecules in the substance. The boiling point of a substance is determined by the strength of the bonds between the atoms and molecules in the substance and the intermolecular forces between the molecules.
Understanding the connection between examples of atoms and molecules and the physical properties of substances is important for many reasons. For example, this understanding can be used to design new materials with specific properties. It can also be used to understand the behavior of substances in different environments.
Building blocks of life
Examples of atoms and molecules are the building blocks of life. They make up everything in living organisms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whales. Atoms and molecules are responsible for the structure, function, and reproduction of all living things.
- Components of living organisms
The human body is made up of about 60% water. The other 40% is made up of organic molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. These molecules are made up of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements.
- Functions of living organisms
Atoms and molecules are responsible for all of the functions of living organisms. For example, proteins are responsible for building and repairing tissues, carbohydrates are responsible for providing energy, and lipids are responsible for storing energy and forming cell membranes.
- Reproduction of living organisms
Atoms and molecules are also responsible for the reproduction of living organisms. DNA and RNA are molecules that contain the genetic information that is passed from parents to offspring.
In conclusion, examples of atoms and molecules are the building blocks of life. They make up everything in living organisms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whales. Atoms and molecules are responsible for the structure, function, and reproduction of all living things.
Essential for technology and medicine
Examples of atoms and molecules are essential for technology and medicine. They are used in a wide variety of applications, from the development of new drugs to the creation of new materials.
- Drug development
Atoms and molecules are used in the development of new drugs. By understanding the structure and function of atoms and molecules, scientists can design new drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
- Medical imaging
Atoms and molecules are used in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRI scans. These techniques allow doctors to see inside the body and diagnose diseases.
- Materials science
Atoms and molecules are used in the development of new materials. These materials are used in a wide variety of applications, from lightweight and durable materials for aircraft to biocompatible materials for medical implants.
- Energy production
Atoms and molecules are used in the production of energy. For example, atoms and molecules are used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
In conclusion, examples of atoms and molecules are essential for technology and medicine. They are used in a wide variety of applications, from the development of new drugs to the creation of new materials. By understanding the structure and function of atoms and molecules, scientists can develop new technologies and medicines that improve our lives.
FAQs about Examples of Atoms and Molecules
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about examples of atoms and molecules, covering their definitions, properties, and applications.
Question 1: What are examples of atoms and molecules?
Answer: Examples of atoms include hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. Examples of molecules include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4).
Question 2: What is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
Answer: An atom is the basic unit of matter, while a molecule is a group of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
Question 3: What are the properties of atoms and molecules?
Answer: The properties of atoms and molecules depend on the types of atoms and the way they are bonded together. Some common properties include mass, density, melting point, and boiling point.
Question 4: What are the applications of atoms and molecules?
Answer: Atoms and molecules are used in a wide variety of applications, including the development of new drugs, the creation of new materials, and the production of energy.
Question 5: Why is it important to study atoms and molecules?
Answer: Studying atoms and molecules is important for understanding the structure and properties of matter, as well as the chemical reactions that occur in the world around us.
Question 6: What are some examples of atoms and molecules in everyday life?
Answer: Examples of atoms and molecules in everyday life include the oxygen we breathe, the water we drink, and the food we eat.
Summary: Examples of atoms and molecules form the basis of all matter and are essential for understanding the chemical reactions that occur in the world around us. Studying atoms and molecules is important for a wide range of scientific disciplines, including chemistry, physics, and biology.
Transition to the next article section: The next section will explore the history of the study of atoms and molecules.
Conclusion
En este artculo, hemos explorado el fascinante mundo de los tomos y las molculas. Hemos aprendido que los tomos son los componentes bsicos de la materia y que las molculas son grupos de tomos unidos por enlaces qumicos. Hemos visto que los tomos y las molculas son esenciales para la vida, la tecnologa y la medicina.
El estudio de los tomos y las molculas es una empresa en constante evolucin. A medida que los cientficos aprenden ms sobre estos bloques fundamentales de la naturaleza, podemos esperar nuevos avances en una amplia gama de campos.
Differences Between Organic And Inorganic Biomolecules: A Guide
Causes Of Bearing Failure: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover Examples Of Atoms, Molecules, And Ions